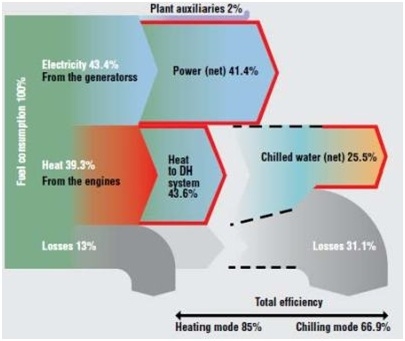
Via CarbonSignal blog comes the following post and Sankey diagram:
“Tri-generation, also known as combined cooling, heat and power (CCHP), is a combination of co-generation, known as combined heat and power (CHP) with an adsorption or absorption chiller to provide water chilling. More information of co-generation can be found here. The chilled water can then be used in refrigeration or air conditioning systems. The engine is connected to a generator which can supply electricity to the site or export electricity to the grid. Typically about 38% of the energy supplied as fuel to the engine is converted to electrical energy.
The rest of the energy leaves the engine as heat via the hot exhaust gases, the coolant system and the oil system. A large amount of the waste heat can be recovered through heat exchangers and can be used to supply all hot water to heat domestic hot water, supply heat to a HVAC system, or supply a chiller to provide all chilled water.
Alternatively the system can be designed to supply a mix of both hot and chilled water to match the site loads. The use of a heat recovery system and chiller can increase the efficiency to between 67- 85% depending on the mix of chilled and hot water required.”